Student Teaching: What It Is and What To Expect

|
Quick Answer Student teaching is a full-time position in which you put your skills to action by observing and teaching in a live classroom. This final phase of a teacher certification program happens under the guidance of a cooperating teacher at your school of choice. Standards will vary, but student teaching placements typically last 14-16 weeks. |
Student teaching is a significant milestone in your professional career. Don’t worry if you are nervous about this final step toward obtaining your teaching certification. All professional teachers undergo this valuable experience of learning and self-reflection.
Each state and program has its own standards and requirements for student teachers, but there are a few common elements. We explain the responsibilities of student teachers, the evaluation process, and how to become one.
What Is Student Teaching?
Student teaching is the final step toward obtaining your teacher certification after completing an undergraduate degree. Typically, student teachers will join a live classroom for one full semester that lasts approximately 14-16 weeks, though placement lengths vary between states and programs. The program will gradually introduce you to teaching responsibilities under the guidance of a mentor — also known as a cooperating teacher or host teacher — who the school will assign.
Joining a live classroom is essential for student teachers to develop professional skills. A successful student teaching placement is necessary to receive a teaching certificate and begin your first year of teaching. Additionally, this experience provides an opportunity to create a network of peers and build employment opportunities for the future.
It’s typical for student teaching positions to receive no pay, but the federal government is reconsidering this due to the teacher shortage. Some states and universities now offer stipends, paid positions, and other incentives, meaning some states are better for teachers than others.
Student Teaching Responsibilities

Student teachers have responsibilities related to personal development, student success, and professional relationships that vary depending on the state and/or program. We outlined the core responsibilities that are typical across most programs.
- Develop and implement daily lesson plans. With the approval of a cooperating teacher, student teachers must develop and implement daily lesson plans that demonstrate content knowledge and the ability to meet students’ needs
- Collaborate with and observe your host teacher or mentor. Student teachers are responsible for building a good relationship with the host teacher by showing interest and asking important questions about their development. Ask your mentor about potential required events like parent/teacher conferences.
- Build relationships with students, peers, and parents. Student teachers must develop positive and productive relationships in the classroom and throughout the school, as student teacher evaluations depend them. Find opportunities to collaborate with colleagues and make a good impression.
- Lead by example and establish proper classroom decorum for students to model. A successful student teacher creates an environment that is conducive to learning and supports all cultures, abilities, and learning styles. Professional dress and manners are your first step in establishing proper classroom decorum.
- Invite feedback from a variety of stakeholders. Student teachers should ask for feedback from staff members and their mentor. They should also take initiative by inviting colleagues to observe their classroom.
- Reflect and develop. Reflecting on professional growth is a responsibility for most student teachers. Self-directed learning is also important, and university-level student teachers need to attend regular academic seminars. Standards differ between states and programs — some student teachers may need to submit weekly journals to their mentors.
- Adapt to the culture. Student teachers should expect to adapt to their school’s culture like eating lunch with fellow teachers and familiarizing themselves with any materials about school culture, such as media release rules. Student teachers should ask their mentors or other faculty for more information.
Tips for Student Teachers
There are many expectations for student teachers, but the experience is collaborative. Focus on what you need to do, and the rest will follow. We’ve outlined helpful tips that will support your success.
1. Prepare
With so many expectations, your ability to prepare makes a difference. Lesson prep is crucial, and you should prepare for more than just the lesson material. It’s essential to have a backup strategy in case your lesson doesn’t resonate with your students.
Request critical information early, such as parent-teacher meeting dates and documents on school rules to impress your mentor. Anticipate important school events, required seminars, and extracurricular activities. Being prepared will give you peace of mind.
2. Arrive Early
Arriving early is a sign of professionalism — and it’s also a common evaluation metric. Being on time might be acceptable, but being early will always impress the people around you. Poor time management can directly impact your final assessment.
Factor in unexpected traffic issues. While these things are out of our control, there’s no excuse for a teacher to miss class. Plan to arrive at least 15 minutes early, or more, depending on your method of transportation.
3. Observe and Collaborate
Collaboration is an important evaluation metric, so you’ll want to create opportunities to work with colleagues. Observe your mentor and other teachers to see various teaching styles. Talk to your mentor and other teachers about lesson plans and teaching in general. By doing so, you will learn from their experience and colleagues will note your initiative.
4. Ask Questions
Student teaching is all about growth, so always ask questions. You need to show improvement, and asking questions is your first step. People will notice and appreciate your dedication.
- Ask students about their school and classroom experiences.
- Ask colleagues for advice on personal and professional development.
- Ask your mentor about upcoming events and meetings.
- Ask your mentor for feedback on anything you like.
- Ask parents about their children and their school experience.
5. Build Relationships
Make an effort to get to know your coworkers. Building relationships can start with joining colleagues for lunch or attending non-mandatory events. Are there playground duties? Volunteer!
Take the time to learn about your students’ interests, needs, and learning styles. Remember their names and create a positive impression on them and your mentor. Use available resources to quiz yourself on names if memorization is a challenge.
6. Snap Photos and Take Notes
You will spend a lot of time observing, especially in your first few weeks. Good documentation will improve your self-directed learning.
Understand your school’s media release and cellphone policies before taking photos. This is particularly important in a K-12 learning environment.
7. Keep a Journal
Some programs require you to keep a journal and submit it. Read your program requirements or speak to your mentor to confirm if this is a requirement.
Even if a journal isn’t required, they’re an extremely useful tool for tracking your growth. Communicating your growth will be part of the final evaluation, and this information will also help improve your ability to interview for teaching jobs.
8. Request Feedback
Don’t be shy about feedback. You aren’t expected to know everything. Requesting feedback demonstrates your commitment to the program.
Your mentor isn’t the only source for feedback. Reach out to other colleagues in your school and consider inviting them to observe you in action. The feedback will be useful and help develop relationships within the school.
9. Expect the unexpected
Creativity and adaptability are paramount in a school setting because every school is full of unique individuals and challenges. Therefore, things are not always predictable.
A lesson plan might not work for the students, and you’ll have to be creative to adapt while continuing to teach. Technology can be unreliable — prepare for challenges that impact your teaching abilities.
10. Treat every day like a job interview
Student teachers share the goal of acquiring professional certification and employment. If you want to become a teacher, treat every day like a job interview
Try to make a genuine impression on your students and colleagues. Speak to the principal about your employment goals during the program. They might connect you with schools in their network or even hire you. Ask students for references to support your future interviews with genuine feedback.
How Are Student Teachers Evaluated?
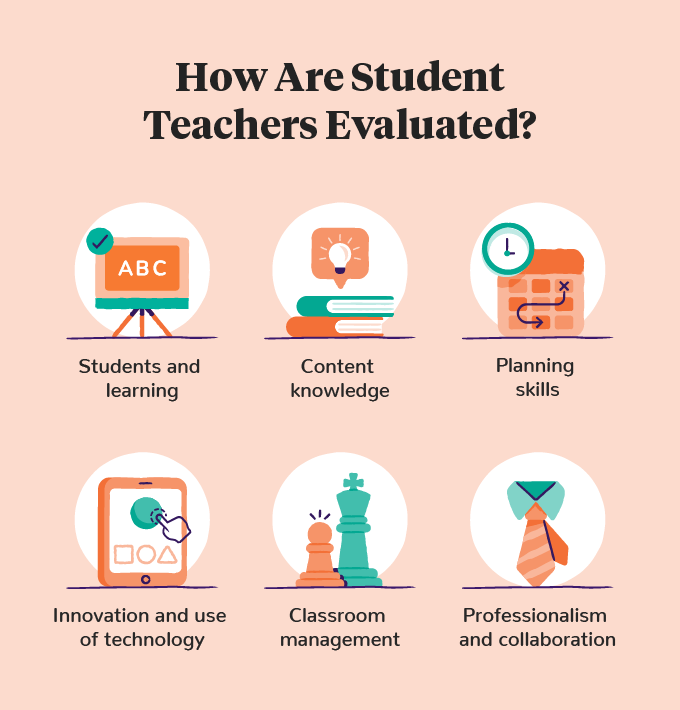
Student teachers typically receive evaluations based on classroom observations made by their cooperating teacher. Although there is no standardized evaluation rubric for student teachers, there are common elements across the states. Assessments are generally graded on a rating scale of one to five. Below are the most typical areas for student teacher evaluation.
- Students and Learning: Student teachers demonstrate an understanding of the developmental levels, learning styles, and cultural differences of students. Evaluations assess the ability to create an environment that is conducive to student learning.
- Content Knowledge: Student teachers must display a thorough understanding of the content and the ability to teach the curriculum in different styles. A good grade means all students received an accessible and challenging learning environment.
- Planning Skills: Developing planning skills is a key part of your collaborative relationship with a mentor. Good lesson prep supports an effective learning environment for all students. The grade will reflect areas such as presentation skills, instructional strategies, organization of materials, interactive techniques, and ability to assess student learning.
- Classroom Management: Effective classroom management combines many of the skills on this list. The final evaluation will assess your ability to minimize disruptions and create a productive environment for students.
- Innovation and Use of Technology: Innovative teaching techniques support different learning styles and accessibility needs. Therefore, innovation and the use of technology are common evaluation standards. The creative application of techniques and technology in the classroom will support the student teacher’s grade.
- Professionalism and Collaboration: This grade reflects the student teacher’s growth as a professional within the program. Personal reflections on professional development are a part of this evaluation. Professional and collaborative relationships will also impact your final grade.
How to Become a Student Teacher

How do you start student teaching? Student teaching begins after obtaining your degree while you pursue a state-approved teaching certificate. You will work with an advisor to create a plan for placement as a student teacher. Finally, you connect with a mentor and begin your student teaching placement.
Step 1: Earn Your Undergraduate Degree
Before participating in an educator preparation program and receiving your teaching certification, it’s necessary to have an undergraduate degree. While some states have different requirements for those not pursuing a degree in education, but both paths are largely the same.
Education students observe classrooms, but they still require a state-approved teaching certification with student teaching hours. Certain states, such as Arizona, combine this effort by requiring a bachelor’s program that involves preparation training. To determine how long it takes to become a teacher, find your state’s teaching license requirements.
Step 2: Consult with your State Certification Office
Contact your state office responsible for teaching certificates to speak with an advisor. Your state office is responsible for licensing and works with local school districts to ensure placement.
Education students may have the option to speak directly with an advisor in their school. Either way, the certification specialist will work to understand your goals and experience before placing you in a school.
Step 3: Get Assigned to a School and Mentor
You will discuss options for schools in collaboration with the teaching certification specialist. Your desired placement school will assign a suitable mentor at their discretion. Some schools require an interview before deciding.
Once they arrange your placement, consider visiting the school beforehand, if allowed. This can be a great time to get familiar with the school and meet your future colleagues.
Step 4: Align on Teaching Strategy with Your Mentor
The relationship between a mentor and student teacher is collaborative. You will work together on a strategy, and you both must contribute to the relationship.
Ask questions and provide feedback as much as possible. Communication is key to a successful mentoring relationship. You don’t need to be perfect. Your willingness to take on challenges and show leadership is what matters most.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When it comes to education, no question is too big or small. Below, we answer some frequently asked questions about student teaching.
What Is the Purpose of Student Teaching?
Student teaching allows education students to apply their knowledge in a live setting. Student teachers receive valuable feedback from their mentors, peers, and students. The vetting by experienced professionals contributes to the quality of certified educators.
How Long Is Student Teaching?
Student teaching lasts about 14-16 weeks long, which is around the length of a full school semester. The length of a student teaching placement depends on the state and school where it takes place.
Do You Get Paid for Student Teaching?
Not all student teaching positions receive payment, but paid student teaching positions increased to address recent teacher shortages. Some student teachers may receive stipends or part-time earnings.
Remember, every teacher goes through the student teaching experience. Like all the best things in life, it is both challenging and rewarding. And when you’re ready, use our Teacher Certification Exam study guides to succeed. We’ve been there, and we know you have what it takes!